Dunbar Cement Kiln: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{CementKiln|EPR=PPC/E/0020020|id=4}} | [[Dunbar Cement Kiln]] is located in eastern Scotland and is owned by [[Tarmac]]. | ||
[[Category:Cement Kilns]] | {{CementKiln|EPR=PPC/E/0020020|id=4}}[[Category:Cement Kilns]][[File:Dunbar2007 pic.jpg|400px|left|Dunbar Cement Works - source Lisa Jarvis 2007]]__TOC__ | ||
[[File:Dunbar2007 pic.jpg|400px|left|Dunbar Cement Works - source Lisa Jarvis 2007]]__TOC__ | |||
<br clear='left'/> | <br clear='left'/> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
==Raw Materials== | ==Raw Materials== | ||
The primary raw materials are Carboniferous Limestone and Shale from Northeast Quarry. | The primary raw materials are Carboniferous Limestone and Shale from Northeast Quarry. | ||
{{NHLFTable|Permit= | {{NHLFTable|Permit=PPC/E/0020020}} | ||
==Waste Used on Site== | ==Waste Used on Site== | ||
There is no waste return for the Dunbar site to [[SEPA]] available for the most recent year of 2018, but the following schematic and detail on the Tarmac website shows that the site used alternative fuels to substitute over 40% of its energy needs, focused on sewage sludge, liquid wastes and tyres. In early 2019 [[Tarmac]] reported the signing of an agremeent with local waste company [[Hamilton Waste and Recycling]] to supply [[SRF]] to the plant. | There is no waste return for the Dunbar site to [[SEPA]] available for the most recent year of 2018, but the following schematic and detail on the Tarmac website shows that the site used alternative fuels to substitute over 40% of its energy needs, focused on sewage sludge, liquid wastes and tyres. In early 2019 [[Tarmac]] reported the signing of an agremeent with local waste company [[Hamilton Waste and Recycling]] to supply [[SRF]] to the plant. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:30, 15 August 2022
Dunbar Cement Kiln is located in eastern Scotland and is owned by Tarmac.
| Tarmac Ltd, Dunbar Plant | |
 See Cement Kilns → page for a larger UK Wide map. | |
| Waste Licence | PPC/E/0020020 |
| Operator | Tarmac |
| Parent Company | CRH plc |
| Clinker Capacity | 0.9 Mt |
Summary site information collated from a variety of sources.
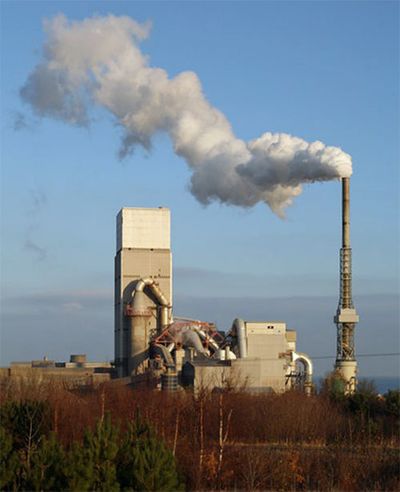

Overview
WikiWaste has used the website Cement Plants and Kilns in Britain and Ireland[1] extensively for the reference material for each individual cement kiln page. The detail on this reference website is extensive and as WikiWaste is focused upon the UK waste and resource market, only the key highlights are captured from this website (and company websites accordingly) to provide background and context. Dunbar started manufacturing clinker in 1963 and up to 2015 had produced 38 million tonnes of clinker through 3 rotary kilns over this period.
Ownership
- 1962 to 2011 Blue Circle
- 2001 to 2013 Lafarge
- 2013 to 2015 Lafarge Tarmac
- 2015 to Present CRH plc (owners of Tarmac)
The Process at Dunbar
The following summary diagram is from Tarmac's website[2]:
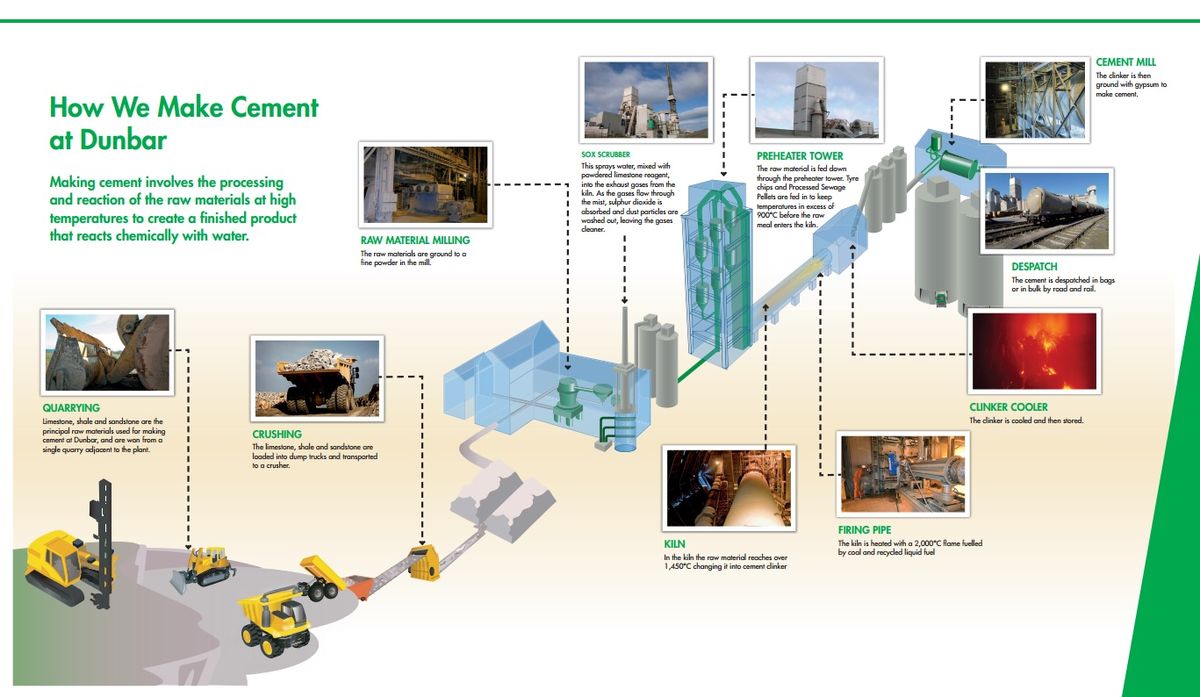
Raw Materials
The primary raw materials are Carboniferous Limestone and Shale from Northeast Quarry.
Waste Tonnage, EWC List
The table shows a list of the Waste for the Permit PPC/E/0020020, that has arrived into sites as reported to the Regulator and then publicised in their reported statistics. The Data used is the most current. The total reported tonnage arriving at the site was: Expression error: Unexpected < operator.t.
| EWC Code | Description | Tonnes In |
|---|
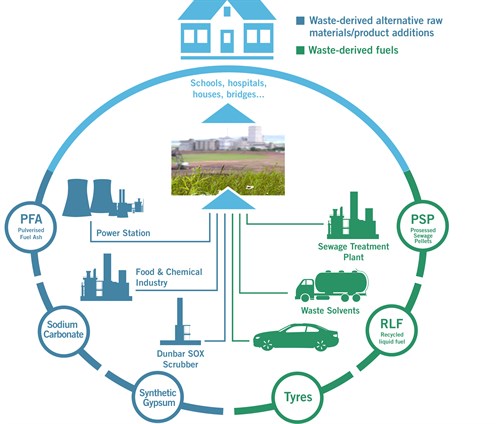
Waste Used on Site
There is no waste return for the Dunbar site to SEPA available for the most recent year of 2018, but the following schematic and detail on the Tarmac website shows that the site used alternative fuels to substitute over 40% of its energy needs, focused on sewage sludge, liquid wastes and tyres. In early 2019 Tarmac reported the signing of an agremeent with local waste company Hamilton Waste and Recycling to supply SRF to the plant. The schematic below from the Tarmac website shows a summary of how materials are used on site[3]:
References
- ↑ https://www.cementkilns.co.uk/index.html
- ↑ How we make cement at Dunbar
- ↑ [1] Dunbar Waste Derived Fuel
