Grate: Difference between revisions
m add categories |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Technologies & Solutions]] | |||
[[Grate]]-type [[Incineration|incinerators]] are suitable for large irregular-shaped [[Waste|wastes]], which can be supported on a stationary or moving alloy [[Grate]] that allows air to pass through from underneath into the [[Waste|waste]]. The primary furnace is followed by a secondary [[Combustion|combustion]] chamber, where additional air and fuel are added, to ensure complete destruction of all toxic emissions. These types of [[Incineration|incinerators]] are widely used for the [[Incineration|incineration]] of solid mixed [[Municipal Solid Waste|municipal waste]] ([[MSW]]), but can also be applied to [[Sewage Sludge|sewage sludge]], [[Clinical Waste|clinical waste]], and [[Commercial and Industrial Waste|commercial and industrial waste]] (C&I)<ref name="ref1">[https://eippcb.jrc.ec.europa.eu/sites/default/files/2020-01/JRC118637_WI_Bref_2019_published_0.pdf Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for Waste Incineration]</ref>. They generally have limited application for [[Hazardous Waste|hazardous waste]] [[Incineration|incineration]] due to the high temperatures required in the chamber which could have adverse effects the structure of the [[Grate]]<ref>[https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123736239500034 Sustainable Industrial Design and Waste Management]</ref>. | [[Grate]]-type [[Incineration|incinerators]] are suitable for large irregular-shaped [[Waste|wastes]], which can be supported on a stationary or moving alloy [[Grate]] that allows air to pass through from underneath into the [[Waste|waste]]. The primary furnace is followed by a secondary [[Combustion|combustion]] chamber, where additional air and fuel are added, to ensure complete destruction of all toxic emissions. These types of [[Incineration|incinerators]] are widely used for the [[Incineration|incineration]] of solid mixed [[Municipal Solid Waste|municipal waste]] ([[MSW]]), but can also be applied to [[Sewage Sludge|sewage sludge]], [[Clinical Waste|clinical waste]], and [[Commercial and Industrial Waste|commercial and industrial waste]] (C&I)<ref name="ref1">[https://eippcb.jrc.ec.europa.eu/sites/default/files/2020-01/JRC118637_WI_Bref_2019_published_0.pdf Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for Waste Incineration]</ref>. They generally have limited application for [[Hazardous Waste|hazardous waste]] [[Incineration|incineration]] due to the high temperatures required in the chamber which could have adverse effects the structure of the [[Grate]]<ref>[https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123736239500034 Sustainable Industrial Design and Waste Management]</ref>. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:16, 23 June 2021
Grate-type incinerators are suitable for large irregular-shaped wastes, which can be supported on a stationary or moving alloy Grate that allows air to pass through from underneath into the waste. The primary furnace is followed by a secondary combustion chamber, where additional air and fuel are added, to ensure complete destruction of all toxic emissions. These types of incinerators are widely used for the incineration of solid mixed municipal waste (MSW), but can also be applied to sewage sludge, clinical waste, and commercial and industrial waste (C&I)[1]. They generally have limited application for hazardous waste incineration due to the high temperatures required in the chamber which could have adverse effects the structure of the Grate[2].
Components of Grate Incinerators

Grate incinerators typically contain the following components:
- Waste feeder
- Incineration Grate
- Bottom ash discharger
- Incineration chamber and boiler
- Incineration air feeding
- Auxiliary burners
Waste Feeder
The waste is discharged from the storage bunker into the feeding chute by an overhead crane, and then fed into the Grate system by a hydraulic ramp or another conveying system. The filling hopper is used as a continuous waste supplier. It is filled in batches by the overhead crane. As the filling hopper surface is exposed to great stress, materials with high friction resistance are selected such as boilerplates or wear-resistant cast iron.
The junction between the lower end of the filling chute and the furnace consists of a dosing mechanism. The dosing mechanism may be driven either mechanically or hydraulically and its feeding rate is generally adjustable. Different construction methods have been developed for the various types of feeder systems:
- Chain Grates/plate bands
- Feeder Grates
- Variable taper feed chutes
- RAM feeders
- Hydraulic ramp
- Feed screws
Incineration Grate
The roles of the incineration Grate include loosening the materials to be incinerated and transporting the materials to be incinerated in the furnace. The Grate requires good distribution of the incineration air into the furnace. A primary air blower forces incineration air through the small Grate layer openings into the fuel layer. More air is usually added above the waste bed to complete combustion. The residence time of the wastes on the Grate is generally around 60 minutes.
Some fine material (referred to as siftings/riddling) may fall through the Grate which gets recovered in the bottom ash remover or is recovered separately. It can be recycled to the Grate for repeated incineration or removed for disposal. If the siftings are recirculated in the hopper, care is taken not to ignite the waste in the hopper.
Grate cooling is carried out to control metal temperatures and so improve Grate life. The cooling medium can be air or water or other liquids such as oils. The heat absorbed by the liquid cooling medium can be used in the incineration process or supplied to an external process.
Bottom Ash Discharger

The bottom ash discharger is used to cool and discharge solid residue (bottom ash) that forces at the end of the Grate. As well as this, the discharger serves as an air seal for the furnace, as it prevents flue gas emissions and uncontrolled air entry into the furnace.
Water is commonly used to extract the bottom ash and bulky products via water-filled ram-types constructions and belt conveyors. The water used for cooling is separated form the bottom ash at the exit and can be recirculated to the ash discharger. The bottom ash can also be discharged in a dry environment by operating a ram-type discharger without water. In this case, the furnace is air sealed by piling up the bottom ash inlet section. Cooling of the bottom ash is then achieved by air without increasing the temperature of the discharger.
Incineration Chamber and Boiler
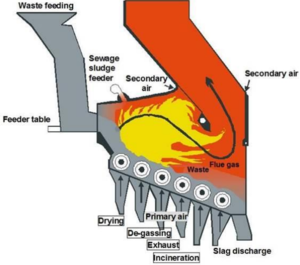
The incineration chamber usually consists of a Grate at the bottom, cooled and non-cooled walls on the furnace sides, and a ceiling or boiler surface heater at the top. The volatile gases produced from the municipal waste are driven off and burn above the Grate with only a small proportion of the actual incineration taking place on the Grate. The following characteristics influence the design of the incineration chamber:
- Shape and size of the incineration Grate
- Sufficient residence time for the flue gases in the hot furnace
- Partial cooling of flue gases by the injection of secondary air

The detailed design of a combustion chamber is usually linked to the Grate type. Its precise design demands certain compromises as the process requirements change with the fuel characteristics. In general, three different designs can be distinguished based on the flow direction of the flue gases in relation to the waste flow: unidirectional current, counter-current and medium current.
Incineration Air Feeding
Air is added at through various inlets in the combustion chamber which is usually described as primary or secondary. Tertiary air and recirculated flue gases are used as well but are less common. Primary air is blown into areas below the Grate which cools the grate bar and caries oxygen into the incineration bed. The secondary air is blown into the chamber to ensure complete incineration of any waste left and intensive mixing of flue gases.
The main roles of the incineration air:
- Provision of oxidant
- Cooling
- Avoidance of slag formation
- Mixing of flue gases
Auxiliary Burners
Auxiliary burners are used at start up to heat the furnace to a required temperature before the waste is introduced. If the temperature falls below the desired value during operation, the burners are switched on automatically. The burners are utilised for shutdown to maintain the furnace temperature and ensure there is no unburnt waste left in the furnace[1].
Different Grate Types
The incineration Grate can be categorised generally by feeder principles: continuous (roller and chain Grates) and discontinuous (push Grates). Grate systems can also be characterised by the way waste is conveyed through zones in the combustion chamber. Each must fulfil requirements regarding primary air feeding, conveying velocity, and mixing of waste. Other features include additional controls or a more robust construction to withstand the severe conditions in the combustion chamber.
Rocking grate
The rocking Grate sections are placed across the width of the furnace. Alternative rows are mechanically pivoted or rocked to produce an upward and forward motion which advances and agitates the waste.
Reciprocating grate
The reciprocating Grate sections span the width of the furnace and are stacked above each other. Alternative Grate sections slide back and forth, while the adjustment sections remain fixed. Waste tumbles off the fixed portion and is agitated and mixed as it moves along the Grate. Different variations of this type of Grate exist, such as some with alternating fixed and moving sections, while others have combinations of several moving sections to each fixed section. In the latter case, the sections can either move together or at different times in the cycle. There are two main variations for reciprocating Grates:
Reverse reciprocating grate
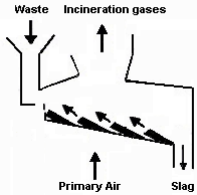
The Grate bars move back and forth in the reverse direction to the flow of waste. The Grate is sloped from the feed end to the ash discharge end and is comprised of fixed and moving grate steps.
Push forward grate
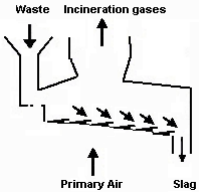
The Grate bars form a series of many steps that move horizontally and push the waste in the direction of the ash discharge.
Travelling grate
The travelling Grate type consists of a continuous metal belt conveyor interlocking linkage that move along the length of the furnace. The reduced potential to agitate the waste (mixing only occurs when waste is transferred from one belt to another) means that it is rarely used in modern facilities.
Roller grate
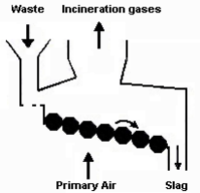
The roller Grate design consists of a perforated roller that traverses the width of the Grate area. Several rollers are installed in series which rolls or tumbles the material forward, towards the ash discharge[1].
Incineration Temperature, Residence Time and Oxygen Content
Incinerators are designed and operated to ensure good burnout of the combustion gases. This is achieved by maintaining the gases at a maximum temperature for a minimum residence time at a minimum oxygen level. Temperature values typically range between 850°C to 1100°C for at least two seconds at a minimum oxygen level of 6%. Higher temperatures can be associated with hazardous waste. The carbon monoxide content of the flue gases is a main indicator of the quality of combustion[1].
