Solid Recovered Fuel: Difference between revisions
m add page specific text |
Additon of text |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Tonnage & Waste Types]] | [[Category:Tonnage & Waste Types]] | ||
Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) is distinct from [[RDF]] in that its quality as a fuel is far | Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) is distinct from [[RDF]] in that its quality as a fuel is far superior. It is typically used in processes that require a high quality, small particle size, high [[Calorific Value]], low [[Moisture Content]] material – such as cement kilns and new-generation [[ATT]] plants. | ||
Solid Recovered Fuels are covered by international technical specifications which set, amongst other parameters, the chemical and physical parameters of an SRF <ref>[https://www.iso.org/committee/5960430.html] ISO/TC 300 Solid Recoverd Fuels </ref> | |||
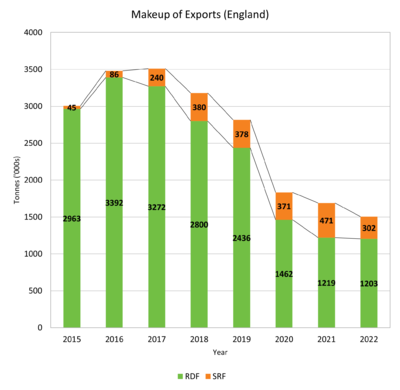
Whilst the data for SRF is often reported within the overall [[Waste Derived Fuel]]/[[RDF]] statistics, there is increasing evidence of a proportional growth in SRF production in the context of a reduction in [[RDF]] export<ref>CIWM Presidential Report 2018 – RDF Trading in a Modern World</ref>. | Whilst the data for SRF is often reported within the overall [[Waste Derived Fuel]]/[[RDF]] statistics, there is increasing evidence of a proportional growth in SRF production in the context of a reduction in [[RDF]] export<ref>CIWM Presidential Report 2018 – RDF Trading in a Modern World</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 12:23, 4 March 2020
Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) is distinct from RDF in that its quality as a fuel is far superior. It is typically used in processes that require a high quality, small particle size, high Calorific Value, low Moisture Content material – such as cement kilns and new-generation ATT plants.
Solid Recovered Fuels are covered by international technical specifications which set, amongst other parameters, the chemical and physical parameters of an SRF [1]
Whilst the data for SRF is often reported within the overall Waste Derived Fuel/RDF statistics, there is increasing evidence of a proportional growth in SRF production in the context of a reduction in RDF export[2].
Typical differences in the key parameters of RDF and SRF mentioned above are broadly as follows:
| Parameter | RDF Example | SRF Example |
|---|---|---|
| CV | 11 MJ/kg | 18 MJ/kg |
| Moisture Content | 25% | 15% |
| Particle Size | 300mm | 40mm |
Increasingly the market is considering further refinement of SRF which has been made into a pellet for ease of storage, haulage, and introduction into a Cement Kiln, with some companies seeking to achieve End of Waste classification that would then enable the material to be used in other applications as a blended substitute for coal - an example of this is Subcoal [3].
References
- ↑ [1] ISO/TC 300 Solid Recoverd Fuels
- ↑ CIWM Presidential Report 2018 – RDF Trading in a Modern World
- ↑ N+P website
