Aberthaw Cement Kiln: Difference between revisions
m add page specific text |
add page specific text |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{CementKiln|EPR=BL3986ID|id=1}} | {{CementKiln|EPR=BL3986ID|id=1}} | ||
[[Category:Cement Kilns]] | [[Category:Cement Kilns]] | ||
[[File:Aberthaw Cement Works1.jpg|400px|left]] | [[File:Aberthaw Cement Works1.jpg|400px|left]]__TOC__ | ||
<br clear='left'/> | <br clear='left'/> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
WikiWaste has used the website <ref>https://www.cementkilns.co.uk/index.html | WikiWaste has used the website Cement Plants and Kilns in Britain and Ireland<ref>https://www.cementkilns.co.uk/index.html</ref> extensively for the reference material for each individual cement kiln page. The detail on this reference website is extensive and as WikiWaste is focused upon the UK waste and resource market, only the key highlights are captured from this website (and company websites accordingly) to provide background and context. Aberthaw started manufacturing clinker in May 1914 (with only [[Rugby]] being older in the UK) and up to 2015 had produced 33 million tonnes of clinker through 6 rotary kilns over this period. | ||
==Ownership== | ==Ownership== | ||
* | * 1912 to 1983 Aberthaw and Bristol Channel Cement Co. Ltd | ||
* 1983 to | * 1983 to 2011 Blue Circle | ||
* | * 2011 to 2013 Lafarge | ||
* 2013 to 2015 Lafarge Tarmac | * 2013 to 2015 Lafarge Tarmac | ||
* 2015 to Present [[CRH plc]] (owners of [[Tarmac]]) | * 2015 to Present [[CRH plc]] (owners of [[Tarmac]]) | ||
==The Process at Aberthaw== | |||
The following summary diagram is from [[Tarmac]]'s website<ref>[https://www.tarmac.com/media/109108/how-we-make-cement-at-aberthaw-lt.jpg How we make cement at Aberthaw]</ref>: | |||
[[File:How-we-make-cement-at-aberthaw-lt.jpg|1200px|left|How we make cement at Aberthaw - Schematic from Tarmac website]]__TOC__ | |||
<br clear='left'/> | |||
==Raw Materials== | |||
The primary raw materials are Blue Lias limestone and clay from the adjacent quarry and Carboniferous Limestone mainly from Glamorgan. | |||
==Waste Used on Site== | ==Waste Used on Site== | ||
The Aberthaw site waste return to the [[EA]] for the most recent year of 2018 showed the following wastes used on site, all of which were used for the primary purpose of substituting fuel requirements in the plant: | |||
{{CKWaste|EPR=BL3986ID}} | {{CKWaste|EPR=BL3986ID}} | ||
The schematic below from the [[Tarmac]] website shows a summary of how materials are used on site<ref>[https://www.tarmac.com/aberthaw-plant/fuels/ Waste Dervived Fuels]</ref>: | |||
[[File:Aberthaw-diagram 520x514.jpg|600px|left|Waste Derived Fuel schematic from Tarmac website]]__TOC__ | |||
<br clear='left'/> | |||
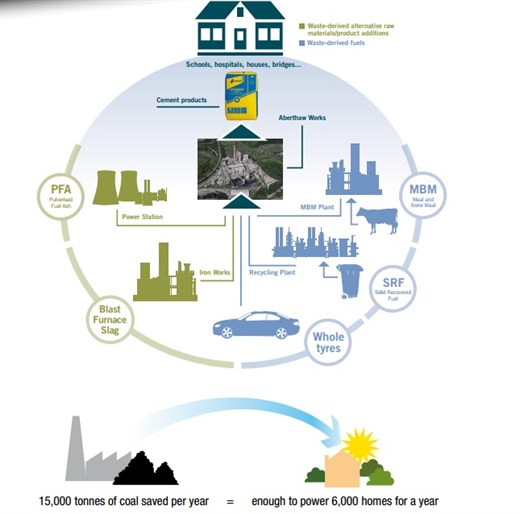
The PFA and Blast Furnace Lag shown in the diagram are not classified as waste by the producer, but as a feedstock for cement production and so tonnages are not reported to the [[EA]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 13:55, 15 April 2020
| Aberthaw Cement Kiln | |
 See Cement Kilns → page for a larger UK Wide map. | |
| Waste Licence | BL3986ID |
| Operator | Tarmac |
| Parent Company | CRH plc |
| Clinker Capacity | 0.5 Mt |
Summary site information collated from a variety of sources.

Overview
WikiWaste has used the website Cement Plants and Kilns in Britain and Ireland[1] extensively for the reference material for each individual cement kiln page. The detail on this reference website is extensive and as WikiWaste is focused upon the UK waste and resource market, only the key highlights are captured from this website (and company websites accordingly) to provide background and context. Aberthaw started manufacturing clinker in May 1914 (with only Rugby being older in the UK) and up to 2015 had produced 33 million tonnes of clinker through 6 rotary kilns over this period.
Ownership
- 1912 to 1983 Aberthaw and Bristol Channel Cement Co. Ltd
- 1983 to 2011 Blue Circle
- 2011 to 2013 Lafarge
- 2013 to 2015 Lafarge Tarmac
- 2015 to Present CRH plc (owners of Tarmac)
The Process at Aberthaw
The following summary diagram is from Tarmac's website[2]:

Raw Materials
The primary raw materials are Blue Lias limestone and clay from the adjacent quarry and Carboniferous Limestone mainly from Glamorgan.
Waste Used on Site
The Aberthaw site waste return to the EA for the most recent year of 2018 showed the following wastes used on site, all of which were used for the primary purpose of substituting fuel requirements in the plant:
| Waste Class | Description | Tonnage Input |
|---|---|---|
| 10 01 02 | coal fly ash | 3,118 |
| 16 01 03 | end-of-life tyres | 6,826 |
| 19 12 01 | paper and cardboard | 6,900 |
| 19 12 10 | combustible waste (refuse derived fuel) | 2,408 |
The schematic below from the Tarmac website shows a summary of how materials are used on site[3]:
The PFA and Blast Furnace Lag shown in the diagram are not classified as waste by the producer, but as a feedstock for cement production and so tonnages are not reported to the EA.
