Gasification: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
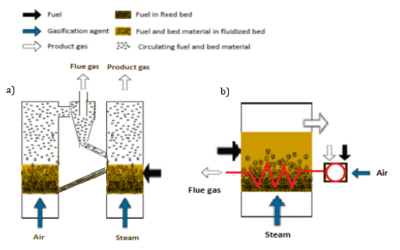
[[File:Allothermal gasifiers.png|400px|right|Different allothermal gasifiers: a)double bed indirect gasifier and b)indirect heat fluidised bed gasifier. All rights reserved.]] | [[File:Allothermal gasifiers.png|400px|right|Different allothermal gasifiers: a)double bed indirect gasifier and b)indirect heat fluidised bed gasifier. All rights reserved.]] | ||
Allothermal/ indirect fluidized beds can have different combinations of fluidization types in the two beds, such as two stationary fluidized bed reactors, one stationary fluidized bed gasifier and circulating bed combustor, one circulating fluidized bed gasifier and one stationary bed combustor or two circulating fluidized beds. Indirect double fluidized beds function in the same way as a fluidized bed, the difference being that there is no oxidant, instead typically steam is added to the gasifier, since the energy required is instead provided by hot sand bed material being transferred at high rate from the second, combustor bed. | Allothermal/ indirect fluidized beds can have different combinations of fluidization types in the two beds, such as two stationary fluidized bed reactors, one stationary fluidized bed gasifier and circulating bed combustor, one circulating fluidized bed gasifier and one stationary bed combustor or two circulating fluidized beds. Indirect double fluidized beds function in the same way as a fluidized bed, the difference being that there is no oxidant, instead typically steam is added to the gasifier, since the energy required is instead provided by hot sand bed material being transferred at high rate from the second, combustor bed. | ||
<ref name="ref1" /> | <ref name="ref1" /> | ||
<br clear=all /> | <br clear=all /> | ||
==== Plasma Arc Gasification ==== | |||
[[File:Plasma Arc.png|150px|right|Plasma Arc Gasification Unit. All rights reserved.]] | |||
Plasma arc gasification (PAG) is essentially the same as [[gasification]] except that waste is heated to much higher temperatures (between 1000-5000°C). This is achieved by the use of a plasma arc which is an electrical device made by passing gas through an electrical spark. The plasma arc melts the waste which turns into a vapour. The simple organic materials cool back down into reasonably clean gases (known as the [[syngas]]) and metals and other inorganic wastes fuse together and cool back into solids (known as the vitrified solid waste or slag). The [[syngas]] is piped away and used to generate energy and the slag material is used as an [[Aggregates|aggregate]] or disposed of. A portion of the [[syngas]] produced provides energy for on site turbines which power the electrical arc and so supporting a self-sustaining electrical power system. <ref>[https://www.explainthatstuff.com/plasma-arc-recycling.html Plasma Arc Recycling]</ref> | |||
<br clear=all /> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 10:13, 22 February 2021
Gasification is the thermal breakdown of a material into a gas via partial oxidation under the application of heat. It Involves the sub-stoichiometric oxidation or steam reformation of a substance to produce a gaseous mixture containing two or more of the following: (i) oxides of carbon, (ii) methane and (iii) hydrogen[1]. The gas is then generally burnt to raise steam and create electricity, but many plants are exploring the option of cleaning the gas for use in a gas engine or separating the gas into usable fractions such as hydrogen for use, as an example, of liquid fuels which in turn may be eligible under the RTFO.
Gasification can be considered a process between Pyrolysis and conventional EfW in that it involves the partial oxidation of a substance. This means that oxygen is added but the amounts are not enough to allow the fuel to be completely oxidised and full combustion to occur. The temperatures employed are typically above 650°C. Generally, the Syngas generated from Gasification will have a Net Calorific Value (NCV) of 4-10MJ/Nm3 [2].
History
The gasification concept was originally developed in the early 1800s for the production of town gas which was a gaseous product manufactured from coal. It provided gas for lighting, cooking and heating for the industrialising Europe and North America in the 19th century. The first use of town gas produced via gasification occurred in 1807 where it was used in Pall Mall, London as the first public street lighting.
Gasification moved to producing synthetic fuels and chemicals in the 1920s. The process was used widely during World War II to produce transportation fuels from coal via the Fischer Tropsch Process. It has been used in the last 40-60 years to convert coal and oil into hydrogen for use in the production of fertilisers (mainly ammonia) and for feedstock preparation in the chemical and refinery industries.
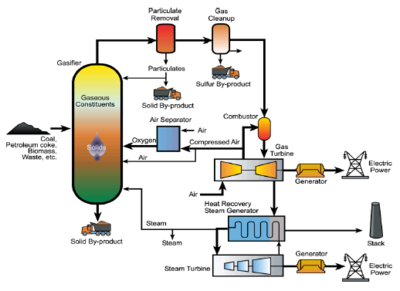
At the start of the 21st century, gasification began commercial scale use by the power industry in Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) plants. IGCC plants convert carbonaceous materials/waste into electricity, with the raw syngas cleaned of particulate matter and pollutants. This emissions free, renewable process allows the production of clean energy while solving waste problems simultaneously. [3]
Autothermal Gasifiers
Autothermal (direct) gasifiers provide the necessary heat of conversion by adding an oxidant to achieve partial oxidation of the fuel within the gasification reactor. This releases energy directly in the reactor where it is consumed. Autothermal conditions are easy to achieve using air or oxygen. Overall the complexity of the process is reduced compared to allothermal gasifiers, however the heat release occurs in the zone of contact between the oxidant and a combustible which requires a good internal heat transfer to even out the temperature or causes a temperature gradient inside the gasifier.
Types of autothermal gasifier:
- Co-current flow (downdraft) moving bed gasifier
- Counter flow (updraft) moving bed gasifier
- Fluidised bed gasifier
- Entrained flow
- Grate gasifier
Co-current flow (downdraft) moving bed gasifier

Downdraft moving bed gasifiers have fuel feeding from the top and the bed formed moves slowly downward while the fuel forming the bed undergoes drying and pyrolysis in fairly well-defined zones as it gradually approaches the lower and hotter parts of the gasifier. The moisture evaporated pyrolysis gases generated also flow downwards co-currently with the moving bed. The oxidant (almost exclusively air) is injected around the circumference of the gasifier just above, or in the throat (the lower part of the gasifier that has a smaller circumference). The air reacts with char and gases present to create an incandescent char bed glow zone at approximately 1 000°C. The tar-laden pyrolysis gases pass through the pores of this glowing bed and the temperature and contact with the char causes decomposition of the tars. In addition, steam and CO2 in the gas react with the char producing additional hydrogen and carbon monoxide. The product gas continues further downward and leaves the gasifier just above the grate at the bottom of the vessel at approximately 800°C which is controlled by the air injection. Ash and unreacted char fall through the grate and are removed.
Counter flow (updraft) moving bed gasifier

In moving bed updraft gasifiers, the oxidant (most often air) is injected at the bottom of the gasifier and the product gas flows upward and exits at the top of the gasifier. In such gasifiers well-defined temperature zones are established, from the fuel drying section at the fuel inlet, the pyrolysis zone beneath the drying zone and the reduction zone where the combustion gases react with the char from pyrolysis and finally the combustion or glow zone at the bottom where the oxidant (air or oxygen combined with steam) is injected. The final burn-out of the char occurs on a moving grate through which the ash falls through into the ash outlet. The hot product gas from the glow zone going upwards is the heat carrier that heats up the fuel to reach the temperature to achieve pyrolysis and the drying prior to extracting the cooler gases at the top at a temperature where excessive tar condensation does not occur (typically at 200-400 °C).
Fluidised bed gasifier
In fluidized bed gasifiers, the reaction space contains a sand-like bed material that is fluidized or entrained by the oxidant gas (air or oxygen), steam or mixtures thereof being added in the bottom. Autothermal or direct gasifiers use an oxidant, and allothermal or indirect gasifiers use steam without an oxidant being fed to the gasifier section.

Stationary (bubbling) fluidized bed material is kept suspended by the gas in a defined bed volume through which gas in the form of interstitial gas and bubbles pass. Above the bed there is a freeboard section used for disengagement of particles mainly ejected by bubbles erupting on the bed surface. This gives a density profile in the reactor of high and uniform density from the fluidizing gas injection level to the top of the bed, and a low density close to the gas density in the freeboard section from the upper bed level to the gas exit.

In a circulating fluidized bed, the gas velocity is higher than for a stationary bed and the bed material or loose clusters of bed material are carried up in the gasifier shaft. By a radial transport some of this material is moved to the wall and transported back to the bottom by gravity as part of the wall layer sliding down (the flow in a large diameter bed establishes a core-annulus type of flow, with the gas-solid suspension flowing upwards and the wall layer moving sand bed moving downwards). The remainder of the solid suspension is carried out by the gas to an external primary particulate separator (typically a cyclone) from which it is returned to the bottom of the gasifier by means of a recycle line with a moving bed of solids.
Entrained flow gasifier

Most entrained flow gasifiers are analogous to the combustion of a solid or liquid fuel or slurry in a burner firing into a combustion chamber. For this reason, the fuel must either be a pumpable liquid that can be dispersed to droplets in the burner nozzle or small particles (< 1 mm) that can be consistently fed by means of dense phase transport to the fuel register of the burner.
Entrained flow gasifier also typically operates in an ash melting mode, i.e. the ash is removed as slag in the bottom of the reactor. This requires operation at very high temperature (1500°C) to reduce the slag viscosity and make it free flowing to avoid build-up of slag in the reactor. The refractory lining of the gasifier should however not be exposed to molten slag. Instead, a protecting layer of solid slag should be formed at the slightly lower temperatures of the wall. This is sometimes assisted by cooling the reactor or parts of it. To reach such high temperatures with low energy content fuels and still retain a significant heating value in the product gas is not possible with air, it requires the use of oxygen mixed with steam.
Grate gasifier

Grate type gasifiers that resemble updraft moving bed gasifiers, i.e. the fuel is moved as a bed on an inclined or moving grate, or on a belt in a furnace tunnel while the oxidant is added from below, such that drying and pyrolysis occurs close to the feed point and burn-out of the char at the ash exit point. This is a kind of cross-flow arrangement where the product gases from all sections in an updraft gasifier is generated separately and then mixed, unlike the counter current passage of the gas from one section through the next in an updraft gasifier.
Allothermal Gasifiers
Allothermal (indirect) gasifiers rely on the fact that the heat necessary for running the gasification reactions is delivered to the gasification reactor from an external source. The heat is generated by combustion and transferred to the gasification with a heat carrier (e.g. circulating bed material) or a heat exchanger (e.g. heat pipe exchanger)[5]. There are two main types of allothermal reactor. One uses a solid heat carrier (sand or larger aggregates) that is circulated between the gasification and combustion reactors, respectively. The hot energy carrier coming into the gasification reactor releases heat to drive the gasifier reactions, and when leaving to the combustion reactor also withdraws a major part of the remaining solid residue (char). The second type is the heat-integrated gasifier, where part of the product gas or char residues are separated from the product gas and are burnt, and via some form of indirect heat exchanger the energy in the hot flue gas is transferred to the gasifier by a combination of radiation and convective heat transport.
Allothermal/ indirect fluidized beds can have different combinations of fluidization types in the two beds, such as two stationary fluidized bed reactors, one stationary fluidized bed gasifier and circulating bed combustor, one circulating fluidized bed gasifier and one stationary bed combustor or two circulating fluidized beds. Indirect double fluidized beds function in the same way as a fluidized bed, the difference being that there is no oxidant, instead typically steam is added to the gasifier, since the energy required is instead provided by hot sand bed material being transferred at high rate from the second, combustor bed.
[4]
Plasma Arc Gasification

Plasma arc gasification (PAG) is essentially the same as gasification except that waste is heated to much higher temperatures (between 1000-5000°C). This is achieved by the use of a plasma arc which is an electrical device made by passing gas through an electrical spark. The plasma arc melts the waste which turns into a vapour. The simple organic materials cool back down into reasonably clean gases (known as the syngas) and metals and other inorganic wastes fuse together and cool back into solids (known as the vitrified solid waste or slag). The syngas is piped away and used to generate energy and the slag material is used as an aggregate or disposed of. A portion of the syngas produced provides energy for on site turbines which power the electrical arc and so supporting a self-sustaining electrical power system. [6]
References
- ↑ DEFRA 2018. Guidance Note for Advanced Conversion Technologies Compliance with the ACT Efficiency Standard criterion in the Contract for Difference scheme. London.
- ↑ DEFRA, 2013. Advanced Thermal Treatment of Municipal Solid Waste. London.
- ↑ Gasification Processes Old and New
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Gasification of Waste for Energy Carriers (IEA Bioenergy)
- ↑ Waste Gasification Process for SNG Production
- ↑ Plasma Arc Recycling
