Refuse Collection Vehicle: Difference between revisions
add page specific text |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
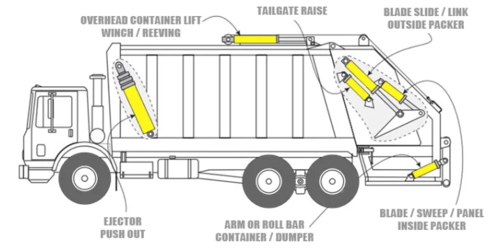
The [[Wheelie Bin]] has a lip on the front edge opposite the hinge of the lid, which locates on a 'comb' lifting unit attached to the rear of the lorry. When the comb is engaged the bin is lifted and pivots on the rear of the lorry, and empties its contents into the rear of lorry. The point of waste deposit into the lorry is called a hopper, and within this unit there is a hydraulic ram that pushes the waste into the body of the lorry via a blade through a series of compacting cycles)(see diagram below). This compaction allows multiple bins of compressible [[Waste|waste]] (such as [[Cardboard]] and/or [[Residual Waste]]) to be emptied and compacted into the lorry to optimise the weight and the logistics associated with onward transportation for processing. At the point of unloading, the rear section of the lorry, including the compacting hopper unit, opens upwards at the rear of the lorry, and a separate hydraulic ram is then used to push the collected waste out of the vehicle. | The [[Wheelie Bin]] has a lip on the front edge opposite the hinge of the lid, which locates on a 'comb' lifting unit attached to the rear of the lorry. When the comb is engaged the bin is lifted and pivots on the rear of the lorry, and empties its contents into the rear of lorry. The point of waste deposit into the lorry is called a hopper, and within this unit there is a hydraulic ram that pushes the waste into the body of the lorry via a blade through a series of compacting cycles)(see diagram below). This compaction allows multiple bins of compressible [[Waste|waste]] (such as [[Cardboard]] and/or [[Residual Waste]]) to be emptied and compacted into the lorry to optimise the weight and the logistics associated with onward transportation for processing. At the point of unloading, the rear section of the lorry, including the compacting hopper unit, opens upwards at the rear of the lorry, and a separate hydraulic ram is then used to push the collected waste out of the vehicle. | ||
[[File:Screenshot 2022-07-26 191746.png|500px|left|Rear Loader Refuse Truck and Hydraulics Layout, all rights reserved Wastebuilt and Eagle Hydraulics]] | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |||
| [[File:Screenshot 2022-07-26 191746.png|500px|left|Rear Loader Refuse Truck and Hydraulics Layout, all rights reserved Wastebuilt and Eagle Hydraulics]] ||{{#ev:youtube|nJYeeToFu0o|450|inline}} | |||
|- | |||
|'''Cross Section Example of RCV Showing Hydraulic Rams'''||'''Video Footage of RCV by Hyva''' | |||
|} | |||
==Other Configurations== | ==Other Configurations== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 39: | ||
==Sizes== | ==Sizes== | ||
The overall size of an [[RCV]] can be specified according to the chassis size (and is expressed in terms of weight of the vehicle) and intended bodies that sit on the chassis. The choice may therefore reflect the configuration of the [[RCV]] required, or often is a reflection of the width and access limits on a collection route - for example smaller narrow bodied vehicles for inner-city restricted access or country lanes in more rural areas. | The overall size of an [[RCV]] can be specified according to the chassis size (and is expressed in terms of weight of the vehicle) and intended bodies that sit on the chassis. The choice may therefore reflect the configuration of the [[RCV]] required, or often is a reflection of the width and access limits on a collection route - for example smaller narrow bodied vehicles for inner-city restricted access or country lanes in more rural areas. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:800.jpg|350px|left|Isuzu 7.5 tonne RCV , all rights reserved HGV traders]] || [[File:5I4D2191.jpg|350px|left|Fulongma 18 tonne RCV. all rights reserved Fulongma]] ||[[File:900.jpg|350px|left|Dennis 26 tonne RCV, all rights reserved HGV Traders]] | |||
|- | |||
|'''7.5 Tonne Truck - note single axle at rear'''||'''15 and 18 tonne Truck - note single axle at rear'''||'''26 Tonne Truck - note twin axle at rear''' | |||
|} | |||
Revision as of 12:32, 2 August 2022
An RCV or Refuse Collection Vehicle is a type of lorry used to empty Wheelie Bins at a waste producers' premises without the removal of the Wheelie Bin from the site. The lorry works in a similar way to a REL Lorry but uses a 'comb' lifting device that hooks under the lip of Wheelie Bin (see Wheelie Bin WikiWaste page) to allow it be lifted and emptied into the rear of the lorry (hence it is also sometimes called a 'rear end loader'). An RCV can lift two smaller Wheelie Bins such as a 240 litre capacity, or one larger Wheelie Bin such as a 1100 litre capacity. A Kerbside Collection Lorry can also be termed an RCV but this type of lorry is separately listed on WikiWaste.

Summary
An RCV or Refuse Collection Vehicle is a type of lorry used to empty Wheelie Bins at a waste producers' premises without the removal of the Wheelie Bin from the site. The lorry works in a similar way to a REL Lorry but uses a 'comb' lifting device that hooks under the lip of Wheelie Bin (see Wheelie Bin WikiWaste page) to allow it be lifted and emptied into the rear of the lorry (hence it is also sometimes called a 'rear end loader'). An RCV can lift two smaller Wheelie Bins such as a 240 litre capacity, or one larger Wheelie Bin such as a 1100 litre capacity. A Kerbside Collection Lorry can also be termed an RCV but this type of lorry is separately listed on WikiWaste.
Process
The Wheelie Bin has a lip on the front edge opposite the hinge of the lid, which locates on a 'comb' lifting unit attached to the rear of the lorry. When the comb is engaged the bin is lifted and pivots on the rear of the lorry, and empties its contents into the rear of lorry. The point of waste deposit into the lorry is called a hopper, and within this unit there is a hydraulic ram that pushes the waste into the body of the lorry via a blade through a series of compacting cycles)(see diagram below). This compaction allows multiple bins of compressible waste (such as Cardboard and/or Residual Waste) to be emptied and compacted into the lorry to optimise the weight and the logistics associated with onward transportation for processing. At the point of unloading, the rear section of the lorry, including the compacting hopper unit, opens upwards at the rear of the lorry, and a separate hydraulic ram is then used to push the collected waste out of the vehicle.
Other Configurations
The body of an RCV can be configured to collect multiple materials, something which has become more common since the early 2000's. This might include, for example, a split body to facilitate a Twin Stream Collection and/or an additional separate non-compacting section for food waste at the front of the lorry (often known as a 'pod') with its own lifting device on the side of the RCV as shown in the pictures below:
Split Body

Example of Split Body RCV for Twin Stream Collection
'POD' Configuration

Example of 'pod' on front of on RCV for Food Waste Collection
Rotopress

Example of Rotopress RCV
{{#ev:youtube|UHXJPCBpkTc|450|inline|Faun Rotopress System|frame}}
Sizes
The overall size of an RCV can be specified according to the chassis size (and is expressed in terms of weight of the vehicle) and intended bodies that sit on the chassis. The choice may therefore reflect the configuration of the RCV required, or often is a reflection of the width and access limits on a collection route - for example smaller narrow bodied vehicles for inner-city restricted access or country lanes in more rural areas.