Hydrothermal Liquefaction: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===== Dry Feedstock ===== | ===== Dry Feedstock ===== | ||
[[File:Dry Feedstock.png|500px|right|Process flow diagram of HTL process of lignocellulose biomass. All rights reserved.]] | [[File:Dry Feedstock.png|500px|right|Process flow diagram of HTL process of lignocellulose biomass. All rights reserved.]] | ||
The tangled properties of dry [[biomass]] give it a complex and rigid crystallinity structure which makes it tougher to process. Despite, the intrinsic source of hydrogen and carbon, the processing of the lignocellulose [[biomass]] is limited due to the substantial amount of the oxygen. [[Wood]]/woody [[biomass]]/lignocellulose is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Cellulose is a long chain polysaccharide with high molecular weight and high degree of polymerisation due to the monomer glucose molecules being stiffly bonded by strong intra– and inter-molecular interactions. Hemicellulose is a branched structure hetero polymer with amorphous structure consisting of pentose and hexose as a polymer and is weaker in comparison to cellulose. Lignin possess similar morphological characteristic of amorphous form as hemicellulose, less solubility similar to cellulose and behaviour of hydrophobic nature | The tangled properties of dry [[biomass]] give it a complex and rigid crystallinity structure which makes it tougher to process. Despite, the intrinsic source of hydrogen and carbon, the processing of the lignocellulose [[biomass]] is limited due to the substantial amount of the oxygen. [[Wood]]/woody [[biomass]]/lignocellulose is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Cellulose is a long chain polysaccharide with high molecular weight and high degree of polymerisation due to the monomer glucose molecules being stiffly bonded by strong intra– and inter-molecular interactions. Hemicellulose is a branched structure hetero polymer with amorphous structure consisting of pentose and hexose as a polymer and is weaker in comparison to cellulose. Lignin possess similar morphological characteristic of amorphous form as hemicellulose, less solubility similar to cellulose and behaviour of hydrophobic nature. | ||
<ref name="ref2" /> | |||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
===== Wet Feedstock ===== | ===== Wet Feedstock ===== | ||
[[File:Wet Feedstock.png|500px|right|Process flow diagram of HTL process of algal/wet biomass. All rights reserved.]] | [[File:Wet Feedstock.png|500px|right|Process flow diagram of HTL process of algal/wet biomass. All rights reserved.]] | ||
Wet [[feedstock]] usually consists of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates and algaenanas. Lipids/fats are non-polar compounds which are immiscible/hydrophobic in nature and composed of fatty acids and glycerol. They are generally soluble in solvents and so the dielectric constant of the solvent in particular water at sub-critical conditions allows the greater miscibility. Proteins is one of the main constituents of algal [[biomass]] which consists of several chains of the monomer amino acid units. They are the building blocks of proteins and highly heterogeneous which presents a challenging process to degrading proteins. Carbohydrates are comprised of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms and are an important source of energy. Among several possibilities of wet [[biomass]], microalgae is considered to be an excellent source of biofuel production due to possessing characteristics of: high photosynthetic efficiency, maximum [[biomass]] production, fast growth rate and lack of arable soil requirements<ref name="ref2" /> | Wet [[feedstock]] usually consists of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates and algaenanas. Lipids/fats are non-polar compounds which are immiscible/hydrophobic in nature and composed of fatty acids and glycerol. They are generally soluble in solvents and so the dielectric constant of the solvent in particular water at sub-critical conditions allows the greater miscibility. Proteins is one of the main constituents of algal [[biomass]] which consists of several chains of the monomer amino acid units. They are the building blocks of proteins and highly heterogeneous which presents a challenging process to degrading proteins. Carbohydrates are comprised of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms and are an important source of energy. Among several possibilities of wet [[biomass]], microalgae is considered to be an excellent source of biofuel production due to possessing characteristics of: high photosynthetic efficiency, maximum [[biomass]] production, fast growth rate and lack of arable soil requirements. | ||
<ref name="ref2" /> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:32, 13 January 2021
Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL) is a thermochemical depolymerisation process in an enclosed reactor to convert wet biomass into biocrude oil and chemicals at moderate temperature (200–400°C) and high pressure (10–25 MPa)[1]. This process is synonym of hydrous pyrolysis but compared to pyrolysis, HTL is carried at lower temperatures and heating rates. In other words, hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass is the thermochemical conversion of biomass into liquid fuels by processing in a hot, pressurized water environment for sufficient time to break down the solid bio polymeric structure to mainly liquid components[2]. Water serves as an important reactant. As the reaction condition approaches to the critical point of water, several properties of water are drastically changed and able to bring about fast, homogeneous, and efficient reactions. The product yield and physiochemical properties of an HTL are primarily affected by the types of feedstock, processing conditions (primarily reaction temperature and time), and existence of a catalyst[1].
Biomass Feedstock
The feedstock used for HTL is classified into two types: dry/lignocellulose biomass and wet/algal biomass.
Dry Feedstock
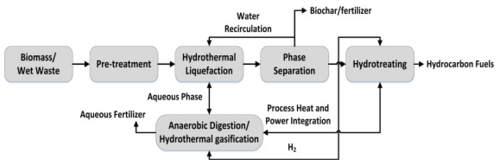
The tangled properties of dry biomass give it a complex and rigid crystallinity structure which makes it tougher to process. Despite, the intrinsic source of hydrogen and carbon, the processing of the lignocellulose biomass is limited due to the substantial amount of the oxygen. Wood/woody biomass/lignocellulose is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Cellulose is a long chain polysaccharide with high molecular weight and high degree of polymerisation due to the monomer glucose molecules being stiffly bonded by strong intra– and inter-molecular interactions. Hemicellulose is a branched structure hetero polymer with amorphous structure consisting of pentose and hexose as a polymer and is weaker in comparison to cellulose. Lignin possess similar morphological characteristic of amorphous form as hemicellulose, less solubility similar to cellulose and behaviour of hydrophobic nature.
Wet Feedstock
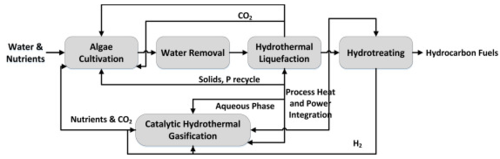
Wet feedstock usually consists of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates and algaenanas. Lipids/fats are non-polar compounds which are immiscible/hydrophobic in nature and composed of fatty acids and glycerol. They are generally soluble in solvents and so the dielectric constant of the solvent in particular water at sub-critical conditions allows the greater miscibility. Proteins is one of the main constituents of algal biomass which consists of several chains of the monomer amino acid units. They are the building blocks of proteins and highly heterogeneous which presents a challenging process to degrading proteins. Carbohydrates are comprised of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms and are an important source of energy. Among several possibilities of wet biomass, microalgae is considered to be an excellent source of biofuel production due to possessing characteristics of: high photosynthetic efficiency, maximum biomass production, fast growth rate and lack of arable soil requirements.
HTL Process Mechanism
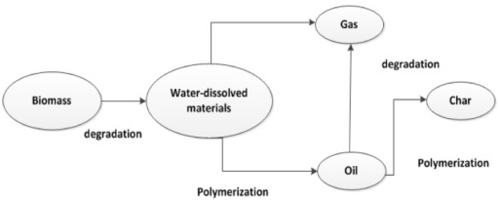
Hydrothermal liquefaction is a biomass to bio-liquid conversion route carried out in water at moderate temperature and high pressures that has a liquid bio crude as main product along with the gaseous, aqueous and solid phase by-products. Many complex reactions take place during the transformation of biomass into crude oil like products due to the complex structures of the feedstocks which are to be broken down. The pathway of HTL comprises three major steps: depolymerisation, decomposition and recombination. Overall, biomass is decomposed and depolymerized into small compounds which may be highly reactive, thus polymerizing and forming bio crude, gas and solid compounds is essential. Also, critical process parameters such as temperature, residence time, the process of repolymerization, condensation and decomposition of the components from the different phases may vary.
- Depolymerisation of biomass is a sequential dissolving of macromolecules through utilization of their physical and chemical properties. The intrinsic hemicellulose and cellulose biopolymers contributes positively towards the thermal stability of the biofuel. Temperature and pressure change the structure of the long chain polymers consisting of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon to shorter chain hydrocarbons. The energy contents of the organic materials are also recycled in the presence of water.
- Decomposition of the biomass monomers involves the loss of water molecule (dehydration), loss of CO2 molecule (decarboxylation) and removal of amino acid content (deamination). The dehydration and decarboxylation facilitate the removal of oxygen from the biomass in the form of H2O and CO2 respectively. Biomass comprising macromolecules are hydrolysed to form polar oligomers and monomers. Water at high temperatures and pressure breaks down the hydrogen bonded structure of cellulose and causes the formation of glucose monomers.
- Recombination and repolymerisation of reactive fragments is the reverse to the initial processing steps due to the unavailability of the hydrogen compound. If hydrogen is freely available for the liquefaction process the free radicals will be capped yielding the stable molecular weight species. On the other hand, if hydrogen unavailability or the concentration of the free radicals are excessively large, the fragments are recombined or repolymerized to form high molecular weight char compounds.
