Thermal Desorption: Difference between revisions
add page specific text |
add page specific text |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Technologies & Solutions]] | [[Category:Technologies & Solutions]] | ||
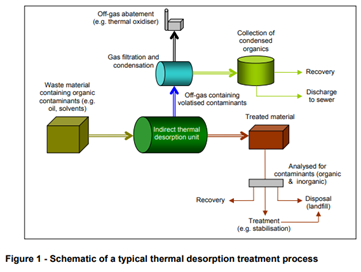
[[Thermal Desorption]] Thermal is a treatment process whereby heat is applied to materials, such as waste soils, [[sediments]], [[slurries]] and [[filter cakes]], in order to remove (vaporise) volatile contaminants (e.g. [[oils and solvents]]). Along with such volatile contaminants, thermal desorption will also vaporise water contained within the material and therefore a thermal desorption plant also functions, and may be referred to, as a “dryer”. A schematic of a typical indirect thermal desorption process is summarised in Figure 1 below<ref | [[Thermal Desorption]] is described in the [[EA]] guidance 382_12 as ''a treatment process whereby heat is applied to materials, such as waste soils, [[sediments]], [[slurries]] and [[filter cakes]], in order to remove (vaporise) volatile contaminants (e.g. [[oils and solvents]])<ref name='EA'>[https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/300893/geho0512bwir-e-e.pdf [[EA]] Guidance 382_12 (an addendum to Guidance S5.06)]</ref>. | ||
==Overview== | |||
[[Thermal Desorption]] is described in the [[EA]] guidance 382_12 as ''a treatment process whereby heat is applied to materials, such as waste soils, [[sediments]], [[slurries]] and [[filter cakes]], in order to remove (vaporise) volatile contaminants (e.g. [[oils and solvents]]). Along with such volatile contaminants, thermal desorption will also vaporise water contained within the material and therefore a thermal desorption plant also functions, and may be referred to, as a “dryer”. A schematic of a typical indirect thermal desorption process is summarised in Figure 1 below''<ref name='EA'/>. | |||
[[File:EA Thermal Desorption Diagram.png|500px|center|EA Thermal Desorption Diagram from Guidance 382_12 : All rights reserved]] | [[File:EA Thermal Desorption Diagram.png|500px|center|EA Thermal Desorption Diagram from Guidance 382_12 : All rights reserved]] | ||
This guidance provides greater detail to the overarching Sector Guidance Note IPPC S5.06<ref>[https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/298118/LIT_8199_dd704c.pdf Guidance for the [[Recovery]] and [[Disposal]] of [[Hazardous Waste|Hazardous]] and [[Non-Hazardous Waste]]]</ref> | |||
==Types of Thermal Desorption Systems== | |||
There are two principle types of approach to introducing heat to the process - either through direct application of heat or indirect application of heat. Sources of indirect heat include natural gas or oil fired burners, thermal oil, electrical (eg infra-red or microwave) and friction<ref name='EA'/>. | |||
Operation mode can be either a batch (ie as a sealed oven) or continuous (ie rotary kiln design)<ref name='EA'/>. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 16:19, 24 June 2021
Thermal Desorption is described in the EA guidance 382_12 as a treatment process whereby heat is applied to materials, such as waste soils, sediments, slurries and filter cakes, in order to remove (vaporise) volatile contaminants (e.g. oils and solvents)[1].
Overview
Thermal Desorption is described in the EA guidance 382_12 as a treatment process whereby heat is applied to materials, such as waste soils, sediments, slurries and filter cakes, in order to remove (vaporise) volatile contaminants (e.g. oils and solvents). Along with such volatile contaminants, thermal desorption will also vaporise water contained within the material and therefore a thermal desorption plant also functions, and may be referred to, as a “dryer”. A schematic of a typical indirect thermal desorption process is summarised in Figure 1 below[1].
This guidance provides greater detail to the overarching Sector Guidance Note IPPC S5.06[2]
Types of Thermal Desorption Systems
There are two principle types of approach to introducing heat to the process - either through direct application of heat or indirect application of heat. Sources of indirect heat include natural gas or oil fired burners, thermal oil, electrical (eg infra-red or microwave) and friction[1].
Operation mode can be either a batch (ie as a sealed oven) or continuous (ie rotary kiln design)[1].
