Plasma
Advanced Plasma reactors convert waste into synthetic gases with the aim of removing unwanted materials and recycling energy. The main component is the gas plasmas which are formed by freeing electrons from gas molecules and atoms using external energy sources. Insignificant emissions of flue gases and very high efficiency in these reactors have created a high incentive for using them. Different types of wastes including municipal, clinical, hazardous, and poisonous, chemical dissolvent, heavy metals, and plastics can be thermally treated using this method[1].
Plasma Incinerator Reactor
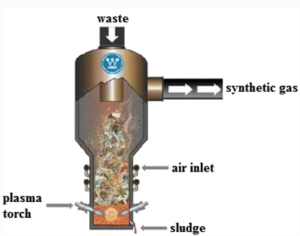
Parts of the plasma reactor explained:
- The waste input at the top where feedstock enters the chamber.
- The lower part holds the feedstock, and also includes the plasma torch. Plasma torches is where the plasma current is created due to the interactions between gases and the electric arc among the electrodes.
- The higher part of the chamber has the capacity to provide enough time for keeping the volatile gases for complete disintegration.
- Synthetic gas outlet which transports the resulting flue gases to create electricity.
- The waste collector and discharger collect the by-products such as bottom ash and sludge which exit the chamber.[1]
