Wood Waste: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
Whilst the macro numbers show 3,362,970 tonnes the general view of several market commentators <ref> , [https://woodrecyclers.org/ Wood Recycling Association website] 4.5mt; [https://www.tolvik.com/published-reports/view/uk-dedicated-biomass-statistics-2017/ Tolvik 2017 Report] 5.0mt and Anthesis (Tolvik report reference unobtainable) 5.7mt</ref> was that the total wood arising was between 4,500,000 and 5,700,000 tonnes in 2014/15 and this can be accounted for a the [[DEFRA]] data being unable to identify wood in the mixed waste streams - this wood then may or may not be pulled out at [[MRF]]s or other similar [[Treatment]] facilities to make this wood available for [[Recycling]] and [[Recovery]]. | Whilst the macro numbers show 3,362,970 tonnes the general view of several market commentators <ref> , [https://woodrecyclers.org/ Wood Recycling Association website] 4.5mt; [https://www.tolvik.com/published-reports/view/uk-dedicated-biomass-statistics-2017/ Tolvik 2017 Report] 5.0mt and Anthesis (Tolvik report reference unobtainable) 5.7mt</ref> was that the total wood arising was between 4,500,000 and 5,700,000 tonnes in 2014/15 and this can be accounted for a the [[DEFRA]] data being unable to identify wood in the mixed waste streams - this wood then may or may not be pulled out at [[MRF]]s or other similar [[Treatment]] facilities to make this wood available for [[Recycling]] and [[Recovery]]. | ||
= | ===Wood Recycling Association=== | ||
==Wood Recycling Association== | |||
In June 2025 the [[Wood Recyclers' Association]] reported their annual statistics on wood waste for 2024 <ref>https://woodrecyclers.org/uk-waste-wood-market-remained-buoyant-in-2024-with-over-96-of-material-processed/</ref> as follows: | In June 2025 the [[Wood Recyclers' Association]] reported their annual statistics on wood waste for 2024 <ref>https://woodrecyclers.org/uk-waste-wood-market-remained-buoyant-in-2024-with-over-96-of-material-processed/</ref> as follows: | ||
* Arisings of wood waste that were broadly at c. '''4.5 million tonnes''' | * Arisings of wood waste that were broadly at c. '''4.5 million tonnes''' | ||
| Line 24: | Line 20: | ||
* 350,000 tonnes went to animal bedding | * 350,000 tonnes went to animal bedding | ||
* Exports with imports netted off to 206,000 tonnes | * Exports with imports netted off to 206,000 tonnes | ||
== Market Overview == | |||
The overall size of the [[Wood Waste]] market in the UK is estimated to be between '''4,500,000 tonnes and 5,000,000 tonnes''', categorized into Grades A to D according to its level of contamination. Where virgin wood is mixed with waste wood such as fence posts, pallets, construction boarding or other waste, the mixed load is considered waste<ref name="foo" />. | |||
[[DEFRA]] figures accounted for 3,362,970 tonnes of wood waste in their most recent 2016 figures, the remaining tonnage being left in mixed waste streams. The separated wood waste is primarily used in animal bedding, as recycled wood panel board and in [[Biomass EfW]]. The use in [[Biomass EfW]] has increased rapidly over recent years from 1,630,000 tonnes in 2017 to around 2,000,000 tonnes in 2018. Whilst tonnage data is presently not available for 2019, if all capacity is delivered in [[Biomass EfW]] plants that are in operation (and ignoring those in development) the capacity would exceed 3,000,000 tonnes, dramatically changing the supply-demand characteristics of the market and sustainability and balance of the overall market. | |||
==Wood Waste Grades== | ==Wood Waste Grades== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
The wood types listed below represent those categories used by local authorities for the wood they manage, primarily at [[HWRC]] sites, which do not correlate with the Grade A to D approach due to the way the data is collected through [[WasteDataFlow]] | The wood types listed below represent those categories used by local authorities for the wood they manage, primarily at [[HWRC]] sites, which do not correlate with the Grade A to D approach due to the way the data is collected through [[WasteDataFlow]] | ||
==Local Authority Tonnage== | |||
===Chipboard and MDF=== | |||
== Chipboard and MDF == | |||
Chipboard is a hard material made out of very small pieces of wood which have been pressed together. It is often used for making doors and furniture<ref>Collins, 2019. [https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/chipboard Definition of chipboard. Collinsdictionary.com.] [online] [Accessed 4 Dec. 2019].</ref>. | Chipboard is a hard material made out of very small pieces of wood which have been pressed together. It is often used for making doors and furniture<ref>Collins, 2019. [https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/chipboard Definition of chipboard. Collinsdictionary.com.] [online] [Accessed 4 Dec. 2019].</ref>. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 66: | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Composite Wood Materials == | ===Composite Wood Materials=== | ||
Wood composites include a range of different derivative wood products, all of which are created by binding the strands, fibers or boards of wood together. It is also referred to as man-made wood, manufactured board, engineered wood, or wood-plastic composite (WPC) when using wood fibers and thermoplastics. They are fixed using adhesives and are engineered to certain specifications, resulting in a material that can have diverse applications<ref name="foo2">Johnson, C. 2017. [https://buildabroad.org/2017/02/22/wood-composite/ Wood Composite - The Alternative, Sustainable Solution to Timber. Build Abroad.] [online] [Accessed 5 Dec. 2019].</ref>. | Wood composites include a range of different derivative wood products, all of which are created by binding the strands, fibers or boards of wood together. It is also referred to as man-made wood, manufactured board, engineered wood, or wood-plastic composite (WPC) when using wood fibers and thermoplastics. They are fixed using adhesives and are engineered to certain specifications, resulting in a material that can have diverse applications<ref name="foo2">Johnson, C. 2017. [https://buildabroad.org/2017/02/22/wood-composite/ Wood Composite - The Alternative, Sustainable Solution to Timber. Build Abroad.] [online] [Accessed 5 Dec. 2019].</ref>. | ||
| | ||
| Line 85: | Line 86: | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Wood == | ===Wood=== | ||
Below is a list of local authorities that send more than 20000 tonnes of this material to a single waste operator. | Below is a list of local authorities that send more than 20000 tonnes of this material to a single waste operator. | ||
{{#clear_external_data:}} | {{#clear_external_data:}} | ||
| Line 101: | Line 102: | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Wood for composting == | ===Wood for composting=== | ||
Below is a list of local authorities that sends more than 2000 tonnes of this material to a single waste operator. | Below is a list of local authorities that sends more than 2000 tonnes of this material to a single waste operator. | ||
{{#clear_external_data:}} | {{#clear_external_data:}} | ||
Revision as of 11:26, 26 June 2025
Wood Waste is wood which is not virgin timber (that is, wood that has been used for any purpose) and associated residues such as off-cuts, shavings chippings and sawdust, either treated or not treated, is waste. They remain waste and subject to waste regulatory control until completely recovered[1]. The overall size of the Wood Waste market in the UK is estimated to be around 4,500,000 tonnes.

Macro Tonnages
DEFRA
The most recent information published by DEFRA [2] is summarized in the pie chart below, with 3,362,970 tonnes of wood generated in the UK in 2016 and is part of the broader tonnage summarized in UK Waste Tonnage:
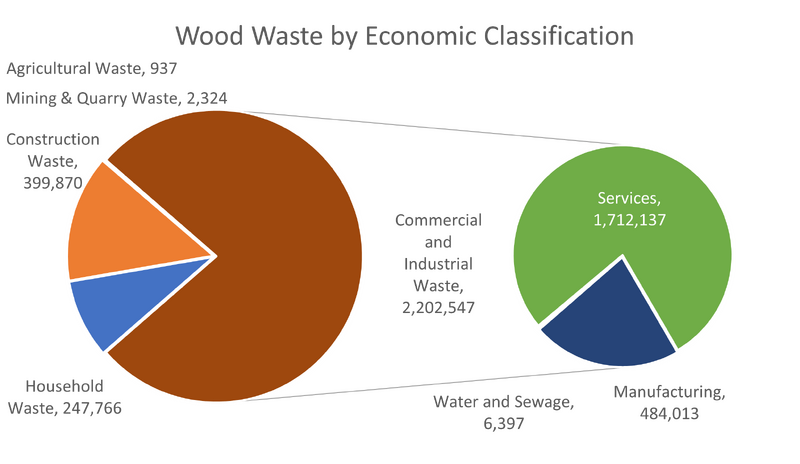
Whilst the macro numbers show 3,362,970 tonnes the general view of several market commentators [3] was that the total wood arising was between 4,500,000 and 5,700,000 tonnes in 2014/15 and this can be accounted for a the DEFRA data being unable to identify wood in the mixed waste streams - this wood then may or may not be pulled out at MRFs or other similar Treatment facilities to make this wood available for Recycling and Recovery.
Wood Recycling Association
In June 2025 the Wood Recyclers' Association reported their annual statistics on wood waste for 2024 [4] as follows:
- Arisings of wood waste that were broadly at c. 4.5 million tonnes
- Processed wood waste was at c. 4.4 million tonnes
- 2.8 million tonnes went to 'Chapter IV compliant biomass facilities' (Biomass EfW)
- Small scale Biomass EfW accounted for 90,000 tonnes per year
- 963,000 tonnes went to panel board manufacture
- 350,000 tonnes went to animal bedding
- Exports with imports netted off to 206,000 tonnes
Market Overview
The overall size of the Wood Waste market in the UK is estimated to be between 4,500,000 tonnes and 5,000,000 tonnes, categorized into Grades A to D according to its level of contamination. Where virgin wood is mixed with waste wood such as fence posts, pallets, construction boarding or other waste, the mixed load is considered waste[1].
DEFRA figures accounted for 3,362,970 tonnes of wood waste in their most recent 2016 figures, the remaining tonnage being left in mixed waste streams. The separated wood waste is primarily used in animal bedding, as recycled wood panel board and in Biomass EfW. The use in Biomass EfW has increased rapidly over recent years from 1,630,000 tonnes in 2017 to around 2,000,000 tonnes in 2018. Whilst tonnage data is presently not available for 2019, if all capacity is delivered in Biomass EfW plants that are in operation (and ignoring those in development) the capacity would exceed 3,000,000 tonnes, dramatically changing the supply-demand characteristics of the market and sustainability and balance of the overall market.
Wood Waste Grades
Treated waste wood is wood that has been treated by being injected, impregnated, sprayed, infused (soaked) or surface coated with any organic or inorganic substances for the purposes of preserving or protecting it or for changing its appearance. Some of these treatments may not be obvious and visible. Surface coating includes varnishes and paints, glues and non-natural veneers[1].
Waste wood is categorized into 4 different types; Grade A-D. This is based on the quality of wood, the utilization of the wood, and type/amount of contaminants[1] with Grade A being primarily clean wood off-cuts, Grades B and C representing increasing quantities of chipboard, MDF and laminated wood with wood off-cuts, and Grade D representing treated wood that is generally classified as Hazardous Waste (although at the present time this is not generally segregated for collection and treatment/disposal in the UK and is mixed with Grade B and C Wood Waste).
The EA Regulatory Position Statement (RPS 207) - 'Classifying wood waste from mixed waste wood sources'[5] applies to all businesses who produce, transport, keep, process, control, use or dispose of waste wood. The RPS was updated on the 27 May 20 and was due to expire on 31 Jan 21 but is now being extended until end of July 2021[6]. RPS 207 permits treated or mixed wood waste (including chipped waste wood and waste fines), which could be classified as hazardous or non-hazardous and has not been assesed and classified in line with the hazardous waste guidance[7] to continue to be classified as non-hazardous. However, the waste wood must be destined for:
- an Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) Chapter IV compliant permitted incinerator or co-incinerator
- the manufacture of board
The RPS does not apply to waste wood that is known and is classified as hazardous such as:
- railway sleepers
- telegraph poles
- wood treated with creosote
which must continue to be segregated and consigned as Hazardous Waste.
The wood types listed below represent those categories used by local authorities for the wood they manage, primarily at HWRC sites, which do not correlate with the Grade A to D approach due to the way the data is collected through WasteDataFlow
Local Authority Tonnage
Chipboard and MDF
Chipboard is a hard material made out of very small pieces of wood which have been pressed together. It is often used for making doors and furniture[8].
MDF is an abbreviation for medium-density fibreboard, it is a wood-substitute material used in interior decoration[9].
Below is a list of local authorities that sends more than 4000 tonnes of this material to a single waste operator.
| Authority | Stream | Facility | Operator | Address | Material | Tonnes | Reporting Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nottinghamshire County Council | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Timberpak Ltd | Cross Green Vale, Cross Green Ind Est, Leeds, West Yorkshire | Chipboard and mdf | 9,188.99 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
| South Lanarkshire | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Not Available | Not Available | Chipboard and mdf | 7,297.03 | Jan21 - Dec21 |
| Cheshire East | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | R Plevin & Sons Ltd | Cheshire Street, Mossley, Ashton Under Lyne, Lancashire | Chipboard and mdf | 6,065.50 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
Composite Wood Materials
Wood composites include a range of different derivative wood products, all of which are created by binding the strands, fibers or boards of wood together. It is also referred to as man-made wood, manufactured board, engineered wood, or wood-plastic composite (WPC) when using wood fibers and thermoplastics. They are fixed using adhesives and are engineered to certain specifications, resulting in a material that can have diverse applications[10]. Wood composites are usually made from the same hardwoods and softwoods used for timber, except when using scraps and wood waste, and are created by mixing ground wood particles with heated thermoplastic resin. Both virgin and recycled thermoplastics are used, with polyethylene-based products being the most common. Composite wood materials are used in a wide range of applications arising mainly from household, industrial and construction sources[10].
Below is a list of local authorities that sends more than 1000 tonnes of this material to a single waste operator.
| Authority | Stream | Facility | Operator | Address | Material | Tonnes | Reporting Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiff County Council | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Other/Exempt | JM ENVIROFUEL; JM ENVIROFUELBerth 31 Wimborne Road, Barry CF63 3DHEPR/AB3690CP | Composite wood materials | 5,308.48 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
| Edinburgh, City of | Source segregated recyclate | Other Method | Not Available | Not Available | Composite wood materials | 3,326.18 | Jan21 - Dec21 |
| Gwynedd Council | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Hadfield Wood Recyclers Ltd | Lumb Lane, Droylsden, Manchester | Composite wood materials | 1,425.93 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
Wood
Below is a list of local authorities that send more than 20000 tonnes of this material to a single waste operator.
| Authority | Stream | Facility | Operator | Address | Material | Tonnes | Reporting Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greater Manchester WDA (MBC) | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Hadfield Wood Recyclers Ltd | Lumb Lane, Droylsden, Manchester | Wood | 42,760.47 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
| Worcestershire County Council | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Dew Mr David & Dew Mr Jonathan | Unit 100, Blackpole Road, Blackpole Trading Estate, Worcester, Worcestershire | Wood | 33,990.98 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
| Hampshire County Council | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Multiple destinations | Multiple | Wood | 26,590.90 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
| Lancashire County Council | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Sita ( Lancashire ) Ltd | Clifton Marsh Landfill Site, Lytham Road, Clifton, Preston, Lancashire | Wood | 22,299.41 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
Wood for composting
Below is a list of local authorities that sends more than 2000 tonnes of this material to a single waste operator.
| Authority | Stream | Facility | Operator | Address | Material | Tonnes | Reporting Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aberdeenshire | Mixed green and food waste | In vessel composting | Not Available | Not Available | Wood for composting | 10,075.66 | Jan21 - Dec21 |
| Dorset Council | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Eco Sustainable Solutions Ltd | Chapel Lane, Parley, Christchurch, Dorset | Wood for composting | 6,425.22 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
| Dorset Council | Source segregated recyclate | Reprocessor - recycling (qu19) | Mark Farwell Plant Hire Ltd | Dow End Farm, Bushes Road, Stourpaine, Blandford Forum, Dorset | Wood for composting | 2,131.98 | Apr21 - Mar22 |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Environment Agency, 2017. Waste Wood Quick Guide 43_17 Issued 02/03/2017. London.
- ↑ UK Statistics on Waste 2020
- ↑ , Wood Recycling Association website 4.5mt; Tolvik 2017 Report 5.0mt and Anthesis (Tolvik report reference unobtainable) 5.7mt
- ↑ https://woodrecyclers.org/uk-waste-wood-market-remained-buoyant-in-2024-with-over-96-of-material-processed/
- ↑ RPS 207, EA May 2020
- ↑ LetsRecycle , Dec 2020
- ↑ Guidance on the classification and assessment of waste. Technical Guidance WM3 V1.1, EA May 2018
- ↑ Collins, 2019. Definition of chipboard. Collinsdictionary.com. [online] [Accessed 4 Dec. 2019].
- ↑ Collins, 2019b. Definition of MDF. Collinsdictionary.com. [online] [Accessed 4 Dec. 2019]
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Johnson, C. 2017. Wood Composite - The Alternative, Sustainable Solution to Timber. Build Abroad. [online] [Accessed 5 Dec. 2019].
